Blepharospasm
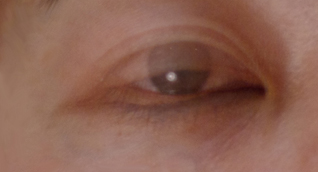
What is blepharospasm?
Blepharospasm is caused by involuntary contraction (dystonia) of the eyelid muscles leading to frequent blinking and sometimes uncontrolled forceful eye closure.
Who does blepharospasm affect and what causes it?
Blepharospasm usually affects people between the age of 50 and 70 years, more commonly in female. For most patients, the underlying cause is not known.
What are some symptoms of blepharospasm?
Patients with blepharospasm often experience light sensitivity and eye discomfort at the onset, followed by increased frequency and intensity of blinking. Some patients can have difficulties opening their eyes, leading to visual impairment despite normal vision. Both eyes are usually affected.
Is there any treatment for blepharospasm?
There is no cure for blepharospasm. Although certain oral medications may help, local injection of botulinum toxin into the eyelid muscle is the most effective treatment. In cases not responding to treatment, eye surgery can be considered.
Does blepharospasm get worse over time?
Symptoms typically progress very slowly and tend to stabilise after two to three years, although intensity of symptoms can fluctuate.

